Japanese doctor's supplement

We deliver products that you can continue to use with peace of mind.
For three decades, our distinguished director, Dr. Makise, has traversed over 85 countries, passionately studying natural substances to bolster health. This journey culminated in the establishment of a clinic in Osaka, Japan. Here, Dr. Makise integrates his unique supplements with his extensive expertise, effectively treating numerous patients contending with intricate health challenges, both domestically and globally. From the forefront of medical innovation, we present products of unparalleled reliability, endorsed by countless users. We are dedicated to consistently delivering supplements that form a dependable cornerstone of your health regimen, safeguarding your well-being today and tomorrow.
We Have Taken Lactoferrin Since Our First Feed.
Breastfeeding is one of the most effective ways to ensure child health, especially in the first year of their life. When it comes to breastfeeding, we cannot and should not forget about colostrums.

Colostrum is a thick and yellowish fluid that precedes breast milk and is the first liquid that breastfeeding babies drink. It is unduly special for a baby in the first few days of life because it has various antibodies, antibacterial, and antiviral agents that protect against different infections and allergies. Colostrum contains a peculiar protein called lactoferrin, necessary for establishing the baby’s immune system. It also helps babies absorb the iron from breast milk.
What is Lactoferrin?
Lactoferrin (LF) is a red glycoprotein found in breast milk. It is also present in exocrine secretions such as tears, nasal fluid, saliva, and gastrointestinal fluid. However, the best source of lactoferrin is colostrum and contains the highest concentrations. For the first week after birth, breastfeeding babies receive between 7 g (=7000 mg) and 10 g (= 10,000 mg) of lactoferrin from colostrum.
Lactoferrin has a strong binding effect on heavy metal ions, particularly iron and copper ions. LF binds to iron quickly and changes its color to red. Hence, after the discovery of lactoferrin, it was called red protein.
Lactoferrin (lacto=milk, ferrin=iron) is a valuable bioactive ingredient that influences biological processes in the human body to provide potential health benefits.
- Enhances the immune system
- Has anti-inflammation and anti-cancer properties
- Supports iron absorption
- Anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, antiviral properties
- Promotes bone health
- Helps with dry eyes
- Potential preventative adjunct for COVID-19
- Prevents damage related to aging
The first immunization of humans
Rich in antibodies, proteins, and other essential nutrients, colostrum serves as the first vaccination for the baby. It protects the baby in various ways, promotes the formation of a healthy gut, and is a natural elixir of life. If we take a closure look, lactoferrin is the main hero within the molecular arsenal of immunity.
Lactoferrin acts as the first line of defense on the immune system, both as a weapon and a moderator. It bridges innate and adaptive immune functions. LF can activate the immune system via cytokine-like signals, causing it to produce antibodies and can intensify natural killer cell activity to enhance immune defense. It is also one of the first factors released by neutrophils upon encountering pathogens.
LF influences the immune cells as most of these cells have LF receptors. It can exert changes on white blood cells by increasing natural killer cells, neutrophils, and macrophage activities. Consequently, the production of cytokine and nitric oxide increases.
Lactoferrin has shown potential in fighting viral and bacterial infections. It also acts as an anti-inflammatory agent. Belonging to the transferrin family, LF has iron-binding properties and maintains the cellular level of iron.
https://www.jpeds.com/article/S0022-3476(16)00294-8/fulltext
A research group at Tottori University in Japan had researched neonatal pigs. They found that, in the newborn piglets, the concentration of lactoferrin in the cerebrospinal fluid increased after the administration of colostrum. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) separates circulating blood and cerebrospinal fluid. The study, in contrast, found that oral administration of lactoferrin transferred to cerebrospinal fluid.
Interestingly, the transportation rate further increased in the post-weaning growth stage and not in the neonate. LF is one of the very few proteins that can effectively pass through the BBB. That is why it may alleviate mental stress and nighttime anxiety.
J Vet Med A Physiol Pathol Clin Med. 49 358-364 2002
Lactoferrin and its iron-binding properties
Iron is essential for many physiological processes in the body. However, it can be potentially harmful in overabundance. It can act as a nutrient for microbial pathogens and promote free radical-induced cellular damage when in excess. Therefore regulation of iron homeostasis is crucial and is primarily regulated at the absorption site in the small intestine.
The iron-binding ability of lactoferrin naturally supports its function in intestinal iron absorption. It belongs to the transferrin family that helps increase iron absorption in the intestine and is also responsible for the delivery of iron to cells.
Its iron-binding capacity also inhibits the growth of several pathogenic bacteria. LF hinders the use of iron necessary for bacterial survival and disrupts the multiplication of these bacteria.
Antimicrobial properties of lactoferrin
Lactoferrin has antimicrobial properties against bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Thus, it is a vital component of the non-specific immune system.
Lactoferrin can prevent bacteria from taking up iron, essential for their functioning. LF can block bacteria’s carbohydrate metabolism and destabilize their cell walls. Besides a broad antimicrobial spectrum against bacteria and fungi, LF also inhibits the replication of a wide range of viruses.
The antiviral activity of lactoferrin is active in the early phase of infection. LF is effective against DNA and RNA viruses, including rotavirus, herpes viruses, and HIV. It exhibits antiviral effects by preventing the entry of viral particles into the host cells, either by blocking cellular receptors or by direct binding to the virus particles.
Lactoferrin as a potential preventative treatment for COVID-19
COVID-19 is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Many COVID-19 patients develop acute respiratory distress syndrome, which leads to pulmonary edema and lung failure and have liver, heart, and kidney damages.
The antiviral properties of lactoferrin make it a great natural supplement for COVID-19. According to a team of researchers led by the University of Huddersfield, LF has the potency to be used as an adjunct for COVID-19 and various other respiratory tract infections. Furthermore, LF possesses unique immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects and may be effective in COVID-19 treatment.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7390755/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34620326/
What makes lactoferrin a super-ingredient?
Lactoferrin has a significant role in the immune system. It influences the immune cells as most of these cells have LF receptors. It can exert changes on white blood cells by increasing natural killer cells, neutrophils, and macrophage activities. Consequently, the production of immune modulators like cytokine and nitric oxide increases.
LF seems to induce a soothing effect in the body, which is why infants almost always fall asleep after nursing. Hence, LF can be used in individuals who have a significant amount of stress. Although sleep can improve physical stress, emotional stress is not that easy to address. Psychological stress is one of the worst things to cope with, and LF can help reduce the burden of this kind of stress. Not only this, LF has various roles throughout the body, which makes it a super-ingredient.
Marker of Inflammation and Infections
Lactoferrin kills bacteria and protects from infections. Therefore, natural lactoferrin levels in our bodies rise during times of infections and inflammation.
Antioxidant Properties
Although iron and copper are necessary minerals for the body, free iron or copper ions act as catalysts to produce hydroxyl radicals. The hydroxyl radical (-OH) is a free radical with the most active chemical properties. It is also known as Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and can severely damage cell membranes. Its oxidative power is greater than the 10th power of 10.
Vitamin C and Vitamin E are natural antioxidants. But, lactoferrin is superior to vitamins C and E in eliminating hydroxyl radicals. LF can bind to these unstable free iron and copper ions, thereby inhibiting the production of hydroxyl radicals. This way, LF reduces oxidative stress and prevents cell damage or cell death.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2915836/
Maintains bone density
Lactoferrin promotes osteoblast (bone-forming cells) growth and inhibits osteoblast apoptosis (the death of bone-forming cells). It inhibits osteoclast precursor cells from differentiating into mature osteoclasts. Through these dual activities, LF can help prevent the loss of bone density.
Lactoferrin and Dry Eyes
Dry eyes are an ever-increasing problem in the current digital era, which has raised in the pandemic. Because lactoferrin exists in tears, the speculation is that it has a role in producing tears. Through its unique combination of antimicrobial action and anti-inflammatory activities, LF in the tear plays a vital role in the maintenance of ocular health.
Cancer treatment support
Lactoferrin supports the immune system by activating microbe and cancer-fighting cells such as natural killer cells and T lymphocytes.
Lactoferrin and interferon
Lactoferrin stimulates interferon production. The inventor of enteric-coated lactoferrin had discovered this fact. Earlier, he had worked in a large pharmaceutical company that produces interferon drugs for hepatitis. As a matter of conscience, he resigned from the drug company because his discovery was potentially financially disadvantageous to the company.
Because lactoferrin is a natural substance, the company could not hold a patent on the discovery. It is very affordable compared to the expensive drugs produced by Big Pharma. It creates the same effect of upregulation of interferon production. LF has the potential to make obsolete extremely costly drugs, which induce the production of interferon.
(Tanaka K, Ikeda M, Nozaki A, et al. Lactoferrin inhibits hepatitis C virus viremia in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a pilot study. Jpn J Cancer Res 90:367-371, 1999).
Lactoferrin should not be confused with whey and colostrums.
People often ask if lactoferrin is more potent than conventional whey protein. Yes, it is. Many of the products used for body-building contain whey protein isolate, which has less than 10% lactoferrin.
Moreover, most of the proteins get denatured during the production process. The lactoferrin contained in these products cannot exert its biological functions adequately. Every year more than 200 scientific papers focusing on lactoferrin are published. But, there are very few articles about whey proteins.
Something to be aware of is that people frequently confuse lactoferrin with colostrum. Colostrum only has small amounts of lactoferrin and doesn’t function in adults.
Are lactoferrin and apolactoferrin the same thing?
Recently, apolactoferrin, a synthetic form of lactoferrin, has been popular on the market. But, this so-called artificial lactoferrin does not contain iron and is basically the original lactoferrin without iron.
Apolactoferrin claims its efficacy with its theory. However, natural lactoferrin has a remarkable effect on our body because it contains 20% iron. It is against the law of nature to remove it. Nature itself, or something as close to nature as possible, is safe and effective most of the time. Hence, we don’t recommend apolactoferrin.
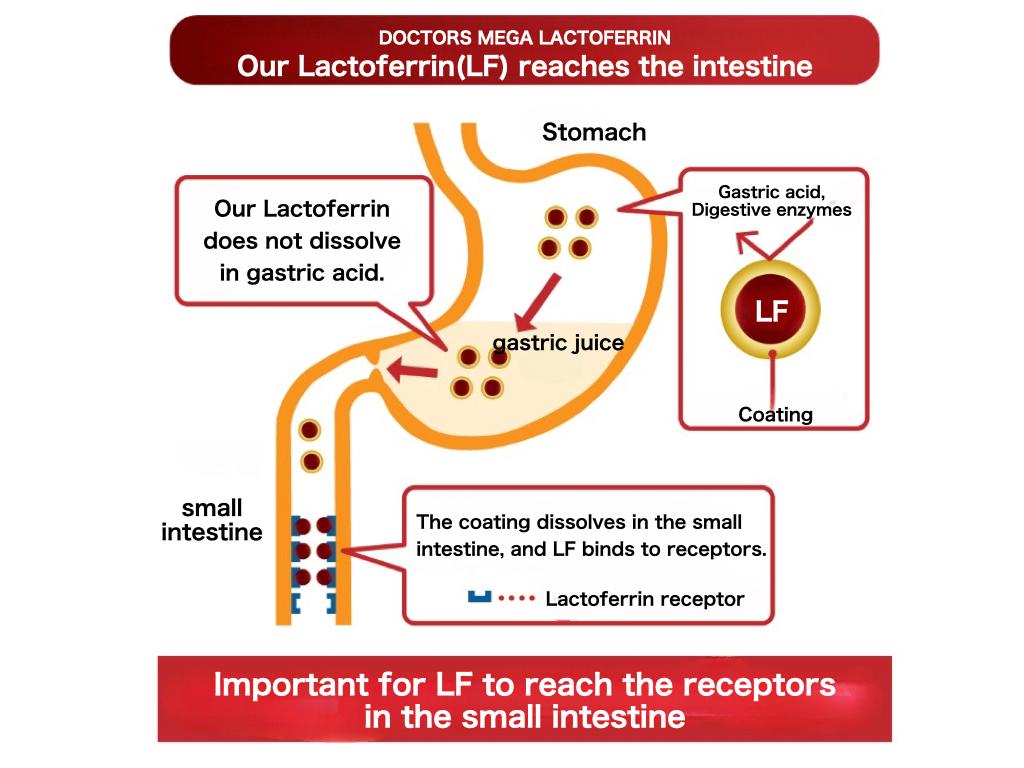
Why is it enteric coated?
Lactoferrin is relatively stable in the gastrointestinal tract in neonates. However, when administered orally to adults, it is degraded and limits its efficacy.
The most important aspect is to inhibit the decomposition of LF in the stomach and duodenum. Using an enteric coating creates a barrier that protects against peptic digestion during oral delivery of lactoferrin. It allows the delivery of a biologically active whole molecule to its optimum site of adsorption or absorption, such as the small intestine.
If lactoferrin cannot reach the small intestine, it is pointless to take it. The breastmilk that infants nurse metabolizes into chunks of curds and whey in their stomachs. Here, the whey with the LF transports to their intestines. That is the only form of lactoferrin that is effective.
The best lactoferrin supplement is enteric-coated. Even though the enteric-coated form of lactoferrin is more expensive, other preparations decompose before they reach the intestine and have no value.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.